Types of Hearing Loss
Brittany Mott
Hearing losses can be categorized into three different types: Sensorineural, Conductive and Mixed Loss.
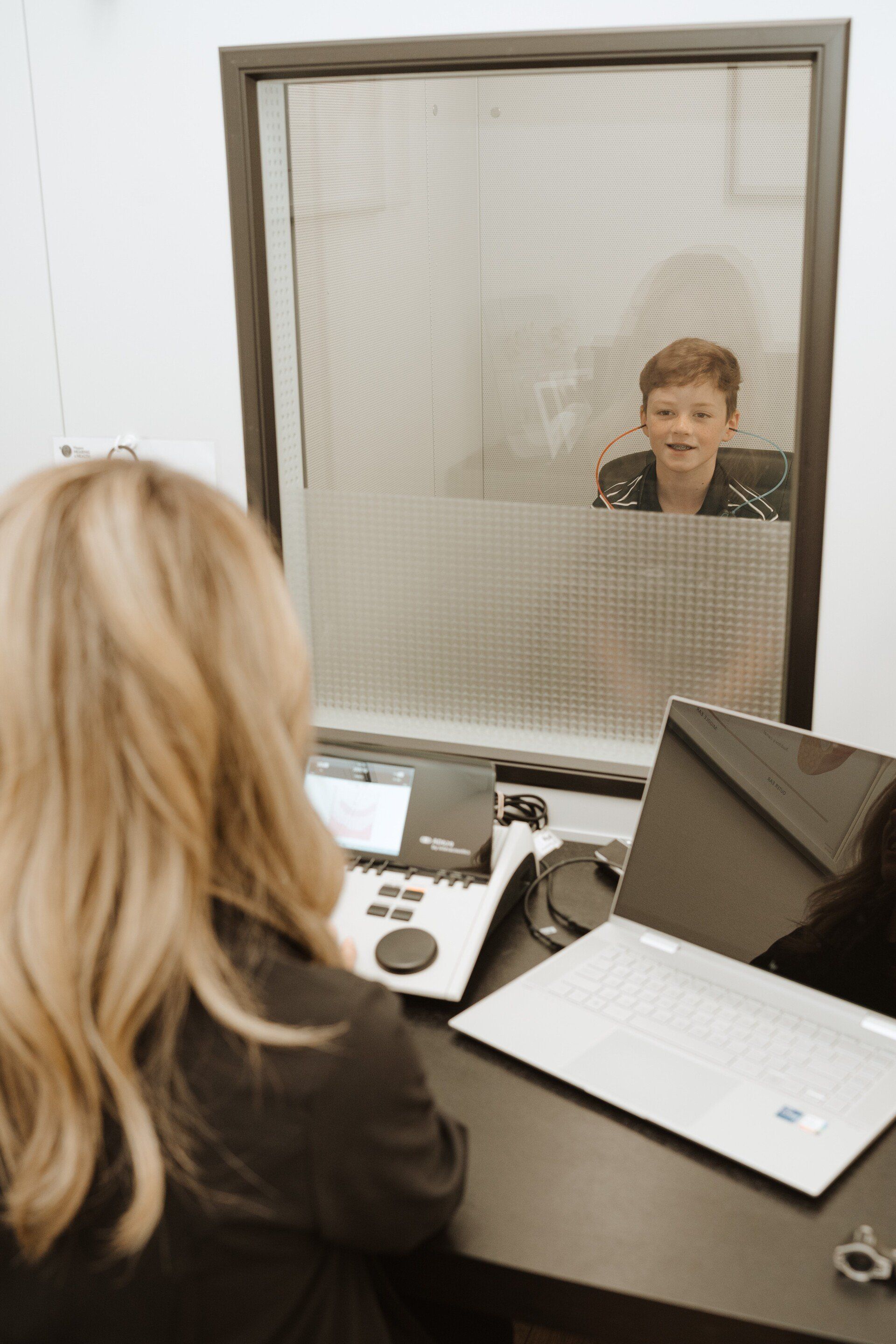
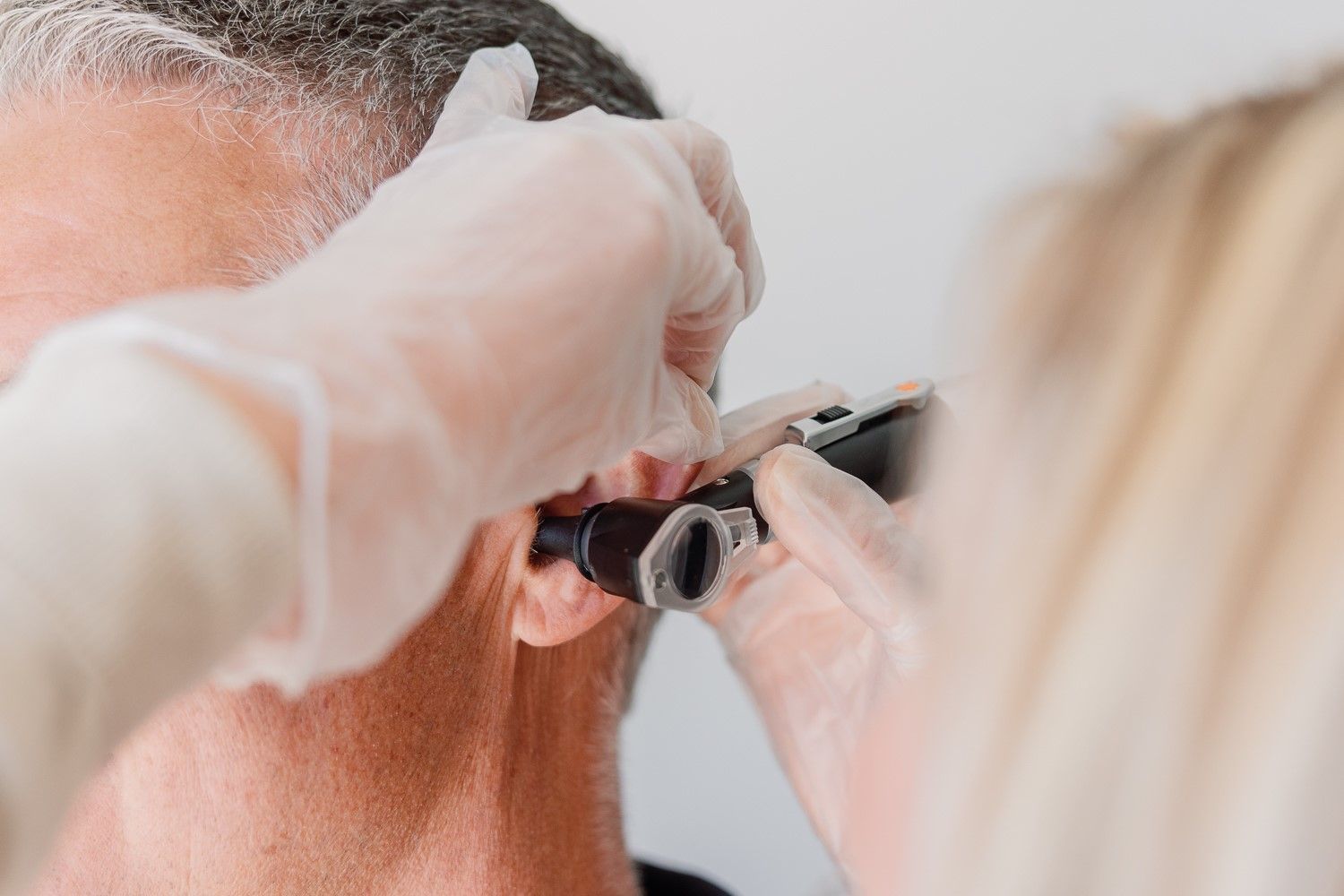
To properly understand your hearing loss, it is first important to understand how you hear. There are three major parts to the ear: the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
All sound is vibration. Sound waves travel through the outer ear, causing the ear drum to vibrate. Vibration of the ear drum set the three bones of the middle ear system (malleus, incus and stapes) into motion, which amplify this vibration to stimulate the tiny hair cells within the inner ear (cochlea) which ultimately translate this vibration into electrical signals to be transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve. Your brain is where these signals are turned into sound and when the brain is not receiving this input, it is referred to as ‘auditory deprivation’.
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing loss in adults. It occurs when there is damage to the hair cells of the inner ear. These hair cells are called stereocilia and can be damaged through exposure to noise, exposure to ototoxic chemicals or drugs, genetic factors or can deteriorate over time. Regardless of the cause, damage to these hair cells will ultimately result in a hearing loss. Hearing loss due to aging is often referred to as presbycusis. Sensorineural hearing loss usually occurs gradually, and one may not notice a hearing loss until it is in the moderate or moderately-severe range of hearing loss. Some early signs of sensorineural hearing loss include:
- Difficulty hearing in noisy environments
- Difficulty hearing women and children
- The feeling that people are ‘mumbling’
- Hearing people speak but not understanding what they’re saying
- Ringing in the ears
Sensorineural hearing loss is treated with the use of hearing aids, or in severe to profound cases, a cochlear implant.
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound cannot pass through the outer or middle ear to the inner ear. In a conductive hearing loss, the hearing at the level of the nerve (inner ear), is within the normal range. Causes of conductive hearing loss include wax buildup in the ear canal (outer ear), foreign object obstruction of the ear drum, perforation of the ear drum, fluid buildup in the middle ear system, otosclerosis, narrowing of the ear canal, tumour of the middle ear, injury resulting in damage to outer or middle ear, deformation of outer or middle ear. Otosclerosis is a condition causing fixation of the stapes due to abnormal bone growth. Ultimately, this disrupts the ability of the middle ear system to transmit sound from the outer ear to the inner ear. As you can see, there are many different causes which can results in conductive hearing loss. The most common symptom of conductive hearing loss is muffled hearing, or the feeling that you are hearing under water. A conductive hearing loss may be able to be alleviated with medical or surgical intervention.
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of a sensorineural and a conductive hearing loss. It is important to determine the type of hearing loss you’re experiencing to determine the best course of treatment for you.
At Niagara Hearing & Health, we have the tools to diagnose your hearing loss and recommend what is best for you.